You’ve got some data in Excel, and you want to summarize it quickly. There’s not much time, and your client or boss needs information right away.
Apply any of these Top 10 Techniques to Summarize Data Quickly with in-built Excel Functions and Features. You’ll get instant results to satisfy most requirements fast.
Microsoft Excel has become the easiest way to analyze data quickly. Several Summary functions, Pivot Tables, What-If Analysis, and other powerful features & methods are available for your use within Microsoft Excel right out of the box. Learn them, and your data analysis will become a breeze.
Here are the Top 10 Ways to Summarize Data in Excel Quickly
These Data Summarization Tips are listed in the order of the easiest to implement to the ones that need a bit more time. Some of the more complex data summarization methods will actually add more value to your data analysis.
- Get The Data Ready For Summarization
- Quick Summary With Auto Functions
- Fast Analysis With Sort & Filter
- Summarize Data With SubTotal Feature
- Summarize Data With an Excel Table
- Using Slicers to Summarize by different dimensions
- Summarize With Excel Pivot Tables
- Summarize Data With Excel Functions
- Advanced Excel Functions for Summarizing Data
- Summarize With Descriptive Statistics From Analysis Toolpak
You can apply the different ways to summarize data based on your familiarity with Excel.
The easiest methods of summarization are listed in the beginning.
And the Pivot Table technique is one of my favorite for a quick and dirty data summarization within Microsoft Excel. It always begins to give me numerous insights into the data.
We cover how to use the Pivot Table to Summarize Data in depth later in this article.
Let’s get started by exploring the different methods of summarizing data.
1. Get The Data Ready For Summarization
Before you begin your summarization, it is important to make sure that your original data is in a good shape.
Duplicate, a blank cell or missing values can often spoil your data summarization.
You need to make sure that the data range is correctly set up before you begin to analyze the data. Also, ensure there is no blank columns in between adjacent cells.

Ensure Proper Column Headings.
For each column, make sure that you have a short and unique column heading. Don’t leave any column without a heading, even though it may be obvious. Column Heading will make it easy to analyze data with any tool in Excel. This way the top row becomes the Header row.
Remove any Duplicates.
Duplicate rows can often sneak in from the data capture sources. So whether you capture data from the Web, or SalesForce, SAP or load from Text or CSV files, the first thing is to clean up the duplicates. To remove duplicates, click within the data range, and go to the Data Menu.
Data > Remove Duplicates.
That’s it, your data will now be cleaner.
Get Rid of Blank Rows:
While blank rows make the data look more readable and easier, it is a bane for data analysis. We do not want blanks to sneak in and skew our averages and other statistical calculations. By sorting the data with the different column headings, the blanks will get separated either to the top or to the bottom. Then you can simply delete these rows if they do not contain any other data points.
Don’t leave blank cells as blanks, specially if there is no value.
It is better to have a 0 than a blank value in any cell. For the text column, if the value is not known, it is better to have a NA (Not Available) showing up.
Having the data cleaned up is the first step in any data analysis. Now you can begin to apply the various data summarization methods.
2. Quick Summary With Auto Functions
The fastest way to summarize data is to calculate the Totals, count the number of entries, find out the average value, and figure out the highest and lowest values.
These 5 functions provide the vital stats of the data. These are the most basic and essential functions… just like a visit to a doctor starts with the nurse checking your vitals – height, weight and blood pressure.

These 5 numbers will provide a quick summary of your data. Here’s how to do this.
Here’s How To Create a Summary Section on Top of Your Data
Calculate SUM: Click on the Autosum icon on the Home tab of Microsoft Office to activate the Sum function of Excel. Then select the data range of the column you want to summarize. Here’s an example:
Calculate COUNT: Click on the drop-down icon on the Autosum button on the Home tab of Microsoft Excel. Choose Count from the list. Then select the data range of the column you want to count. You can use the count function only for numeric columns like Salary, Sales, Quantity etc. using this function. So don’t try this on a text column like Country or Department.
Calculate AVERAGE: Click on the drop-down icon on the Autosum button on the Home tab of Microsoft Excel. Choose Average from the list. Then select the data range of the column you want to Average. You can only average the numeric columns like Quantity, Profit, ROI etc. using this function. Here’s an example:
Calculate Highest Values: Click on the drop-down icon on the Autosum button on the Home tab of Microsoft Excel. Choose Maximum from the list. Then select the data range of the column you want to choose for picking up the highest value. You can only pick numeric columns like Quantity, Profit, ROI etc. using this function. Here’s an example:
Calculate Lowest Values: Click on the drop-down icon on the Autosum button on the Home tab of Microsoft Excel. Choose Minimum from the list. Then select the data range of the column you want to choose for picking up the lowest value. You can only pick numeric columns like Quantity, Profit, ROI etc. using this function.
Calculating the Sum, Count, Average, Min & Max are the fastest ways to get started in your journey to view summary data quickly.
3. Fast Analysis With Sort & Filter
If you sort the data by any key column like Country, Department, Category, Product, Zone, Area etc., then it becomes super easy to analyze data.
To sort the data on any column, follow these steps. Go to
Home > Sort & Filter > Sort A to Z or Sort Z to A.
This will sort the data in your chosen way (ascending or descending) for the column you are in.
Then click on the Filter icon. This will set up auto filters on top of all column headings. Now when you filter on any column, only values for that column will be visible. Unfiltered values are hidden, and visible data corresponds to the Filter selections.
After you have filtered for any particular selection, you can also highlight any numeric column, and see the summary being displayed at the bottom Excel bar.
At one time, you can see the Sum, Count, Average, Maximum & Minimum values from the selected range.

Now you can begin to summarize data for any selection, the way you want it.
4. Summarize Data With Subtotal Command:
If the data is already sorted, you are now ready to explore the Subtotal feature of Excel. This hidden gem has been languishing in Excel since the early 1990s, and very few people use it.
To add subtotals to your summary, first, clear all filters. And then Sort on the column that you want to add subtotal for.
The Subtotal feature is available on the Data tab of Excel.

Go to Data > Subtotal.
Choose the function to perform (Sum, Count, average etc), for the numeric column, and group by the desired column.
As an example, to get the subtotals of the number of employees by each department, it should say: At each change in Department, Count, number of Employees.

Click OK, and you should see the subtotal rows from the data in Excel. In the end, you will also see the Grand Totals calculated.

You can clear the subtotals, and perform the subtotals again at any time. To clear the subtotals, go to Data > Subtotal > Remove All. The subtotals and the Grand total row are all removed completely.
5. Summarize Data With an Excel Table
Microsoft Excel 2007 brought a new feature called Tables, which are amazing at doing simple summarization from a table of data.
To begin, stay within the data range on the Excel sheet. Then click
Home > Format as Table.
Select any colour you prefer, and click OK. Excel automatically recognizes whether the data selection has headers or not.
Now you have a new tab added to the Excel menu, at the end. It is called Table Design.

Select it, and check the Total Row checkbox. Now you have an additional total row added at the bottom of the data. Every column on the total row is a total calculator. Simply click on the dropdown showing in the total row cells, and choose an appropriate summarization – sum, count or average. Now that column will show a total sum or total count or total average of that column.
The great thing is that now if you filter the list, the totals will change dynamically. No need to call the Subtotal function every time. This technique of data summarization is better than the manual methods of subtotal.

Begin using the Table features if you haven’t done so already.
6. Using Slicers to Summarize by different dimensions
Beginning Excel 2010, Microsoft added the Slicers functionality which takes the Tables to greater heights.
Instead of filtering each column one by one, you can now create a slice of the data from the Excel spreadsheet at any time.
Go to Table Design > Insert Slicer > Pick the column of your choice that you want to filter on.

Now you can click on any value in the slicer, and the data is instantly filtered. You can make multiple selections, by holding the control key.
And more than 1 slicer can be added, giving you multiple combinations of slices. The total row updates automatically as each selection is made. This is truly slice and dice of data, allowing you to summarize data in Excel spreadsheets just by using a mouse. No formulas or lengthy steps are involved.
7. Summarize With Excel Pivot Tables
Pivot tables have been in Excel for over 30 years. They are the most used feature of Excel, as it allows for business analysts & managers to manipulate and analyze data in countless better ways.
A pivot table is actually a summary table, which allows you to slice and dice the data by different dimensions.

Pivot tables are easy to get started with.
To create a pivot table, Stay within your dataset. Then go to Insert > Pivot Table. The entire dataset is selected. Click OK and a new pivot table is created in a new worksheet by default.
Click on the column that you want to summarize on, from the pivot table field list on the right side of the screen. In our example, we check the Department and Sales amount from the field list. Instantly, the total sales per department are calculated and populated in the pivot table on the left. Notice that Excel generates a unique list of departments, without any duplicates.
To visualize both the Sum & Count of the data points, you can drag one more copy of the Sales into the Values Area section. Then right-click on the value, and choose
Summarize Values by > Count.
Similarly, you can change the calculation type, and pick up Average, Max, Min. This way, you can have all the vital statistics about your data summarized by each department.
Additionally, to see the percentage of sales done by each department,
Right Click on any numeric value in the pivot table, and choose Show Value As > % of Grand Total.
This will instantly calculate the % of contribution done by each department. The grand total will show 100% of the sales.
It is a good idea to sort the % of Grand Total value from highest to lowest by value, showing the highest values on the top.
You can then add a further selection in the rows or columns, to get a 3D view of your data. As you can see, Pivot Table is a powerful tool that can get the analysis done the fastest!
As you learn more about the Pivot Tables, you’ll realize that they can be used to summarize data from a single worksheet or multiple worksheets.
A pivot can even summarize data from multiple workbooks too. This is a must-learn feature of Microsoft Excel. You can attend an Advanced Excel Training in Singapore at Intellisoft, where I teach this class.
- FREE COURSE ON PIVOT TABLES TO ANALYZE DATA – No Signup is required. Click & Start watching Videos For Free and improve your Pivot Table Skills.
8. Summarize Data With Excel Functions

To get the most flexibility, you can actually write your own summary functions within Excel, by using the following formulas.
We have already covered the Autosum features of Excel which generate the Sum, Count & Average. Now we will look at how to write these functions manually.
To Sum a range of data, use =SUM(range) in the formula bar.
To Count a range of numeric data cells, use =COUNT(range). This generates a numeric count.
To count a range of alpha-numeric data cells, use =COUNTA(range). COUNTA can be used to count both numeric and non-numeric data.
To find the average of any data, use =AVERAGE(range).
9. Advanced Excel Functions for Summarizing Data
The real power of Excel functions is when you go beyond the basic summary functions and do some advanced data analysis.
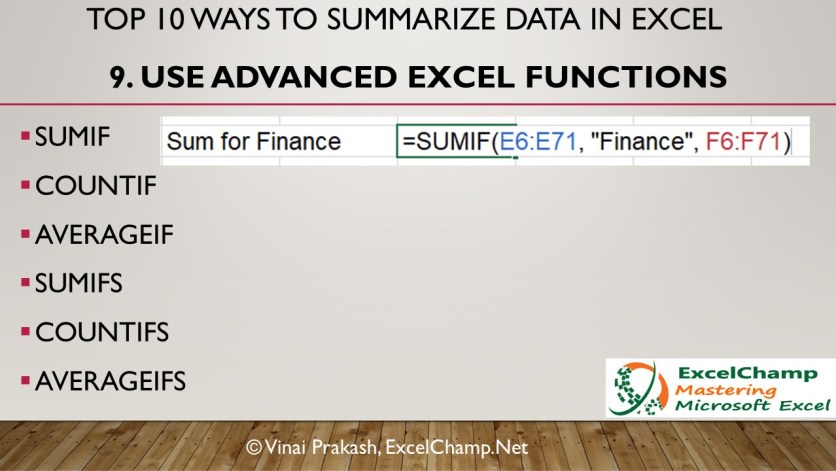 You can use the following Excel formulas
You can use the following Excel formulas
Sum the data conditionally. For example, if we want to summarize the monthly sales only for a particular country, we can use the Excel Sumif function:
=SUMIF(country data range, select_country, monthly sales data range)
Similarly, to count the number of products sold by a country, we can count by using the COUNTIF function of Excel
=COUNTIF(country data range, select_country, monthly sales data range)
And average sales per country can be analyzed by using the following formula of AVERAGEIF.
=AVERAGEIF(country data range, select_country, monthly sales data range)
For multiple, if conditions, you can use the sumifs function to summarize data by your chosen selection. These functions can really cut down your data analysis time when you have large amounts of data to summarize.
10. Summarize With Descriptive Statistics From Analysis Toolpack
Finally, Microsoft Excel has the Data Analysis Toolpak, a hidden Statistical Analysis tool, that can calculate the Median, Standard Deviation, Variance, Analysis of variance (ANOVA), and much more in a single click.
To enable the Data Analysis feature in Excel, you must go to
File > Options > Add Ins.
Then select the Data Analysis ToolPak if it is inactive. You might have to click on the Go button at the bottom. Choose the Toolpak, and click OK. This will add a Data Analysis button on the Data tab of Excel, at the end. Check it out. Once this button is enabled, it stays active, and you can use it subsequently anytime.

To use this Data Analysis ToolPak, go to
Data Analysis > Descriptive Statistics.
Select the Entire numeric column that you want to analyze in the Input Range. Check the Labels in First Row checkbox if your data has a header.
Then check the output box radio button, and key in a cell address where you want the summary statistics to be generated. Check Summary Statistics, and click OK.

The full descriptive statistics are displayed instantly. This final result is a detailed Statistical Analysis of your data.

Multiple Ways to Summarize Data in Excel – Conclusion
There are so many different ways to summarize data in Excel. Mastering them will improve your data analysis skills, and you will be on your way to huge success, by taking action on the insights gleaned from your data analysis.

Go ahead and try them out.
Each technique is a gem, and adds to your skills in Excel data analysis.
Cheers,
Vinai Prakash
About Vinai Prakash: Vinai is a prolific speaker, author, entrepreneur and coach on the topics of Data Analytics, Project Management, Advanced Excel Techniques, SQL, Python, Data Visualization with Power BI & Creating of Excel Dashboard and several other soft skills. He is one of the Best Trainers for Data Analytics Training and is highly sought after for his advice. Contact Vinai for your next Data Analysis Training.
- Join Vinai’s Data Analysis With Excel MasterClass, and learn how to analyze data firsthand.

